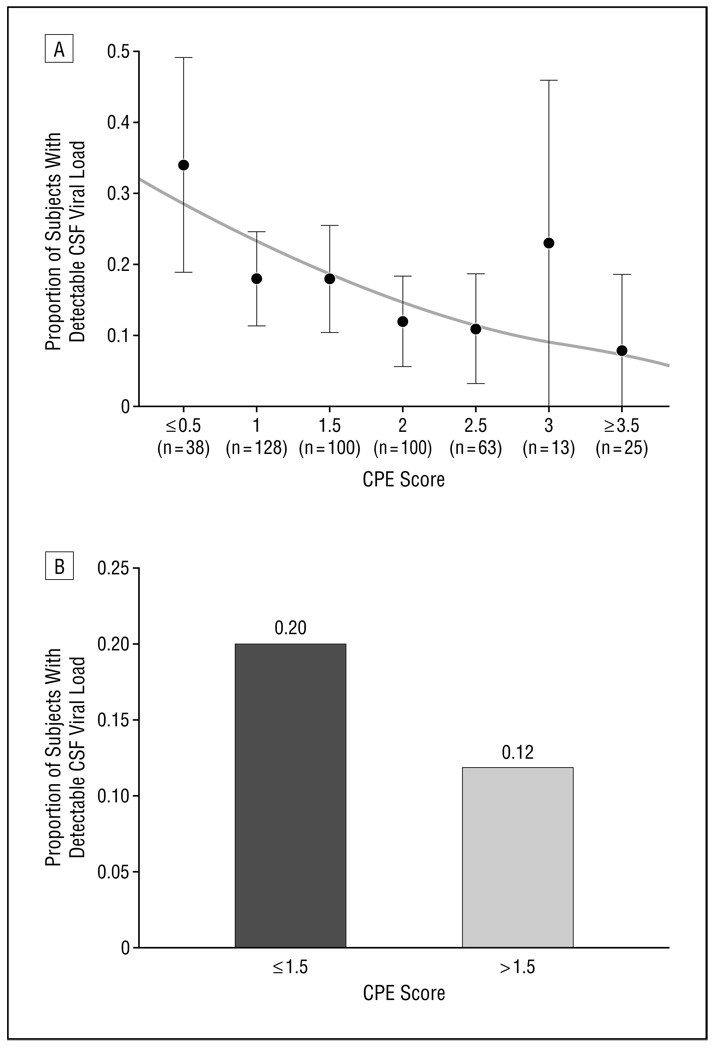
Validation of the CNS Penetration-Effectiveness rank for quantifying antiretroviral penetration into the central nervous system.
OBJECTIVETo consider whether or not penetration of a mix routine into the central nervous system (CNS), as estimated by the CNS Penetration-Effectiveness (CPE) rank, is related to decrease cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) viral load.
METHODSData had been analyzed from 467 contributors who had been human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) seropositive and who reported antiretroviral (ARV) drug use. Individual ARV medicine had been assigned a penetration rank of 0 (low), 0.5 (intermediate), or 1 (excessive) primarily based on their chemical properties, concentrations in CSF, and/or effectiveness in the CNS in medical research.
The CPE rank was calculated by summing the particular person penetration ranks for every ARV in the routine.RESULTSThe median CPE rank was 1.5 (interquartile vary, 1-2). Lower CPE ranks correlated with greater CSF viral hundreds. Ranks lower than 2 had been related to an 88% enhance in the odds of detectable CSF viral load.
In multivariate regression, decrease CPE ranks had been related to detectable CSF viral hundreds even after adjusting for complete quantity of ARV medicine, ARV drug adherence, plasma viral load, period and kind of the present routine, and CD4 rely.
CONCLUSIONSPoorer penetration of ARV medicine into the CNS seems to permit continued HIV replication in the CNS as indicated by greater CSF HIV viral hundreds. Because inhibition of HIV replication in the CNS might be essential in treating sufferers who’ve HIV-associated neurocognitive issues, ARV remedy methods that account for CNS penetration must be thought of in consensus remedy tips and validated in medical research.
Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969-2000).
It is now nicely established that the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is the principal 8-9 nm intermediate filament in mature astrocytes of the central nervous system (CNS).
Over a decade in the past, the worth of GFAP as a prototype antigen in nervous tissue identification and as an ordinary marker for elementary and utilized analysis at an interdisciplinary stage was acknowledged (Raine, 135).
As a member of the cytoskeletal protein household, GFAP is considered essential in modulating astrocyte motility and form by offering structural stability to astrocytic processes.
In the CNS of greater vertebrates, following damage, both in consequence of trauma, illness, genetic issues, or chemical insult, astrocytes grow to be reactive and reply in a typical method, termed astrogliosis.
Astrogliosis is characterised by fast synthesis of GFAP and is demonstrated by enhance in protein content material or by immunostaining with GFAP antibody. In addition to the main utility of GFAP antisera for routine use in astrocyte identification in the CNS, the molecular cloning of the mouse gene in 1985 has opened a brand new and wealthy realm for GFAP research.
These embody antisense, null mice, and quite a few promoter research. Studies exhibiting that mice missing GFAP are hypersensitive to cervical spinal twine damage attributable to sudden acceleration of the head have supplied extra direct proof for a structural position of GFAP. While the structural operate of GFAP has grow to be extra acceptable, the use of GFAP antibodies and promoters proceed to be worthwhile in finding out CNS damage, illness, and growth.
