Morphological Characteristic Regulation of Ligninolytic Enzyme Produced by Trametes polyzona.
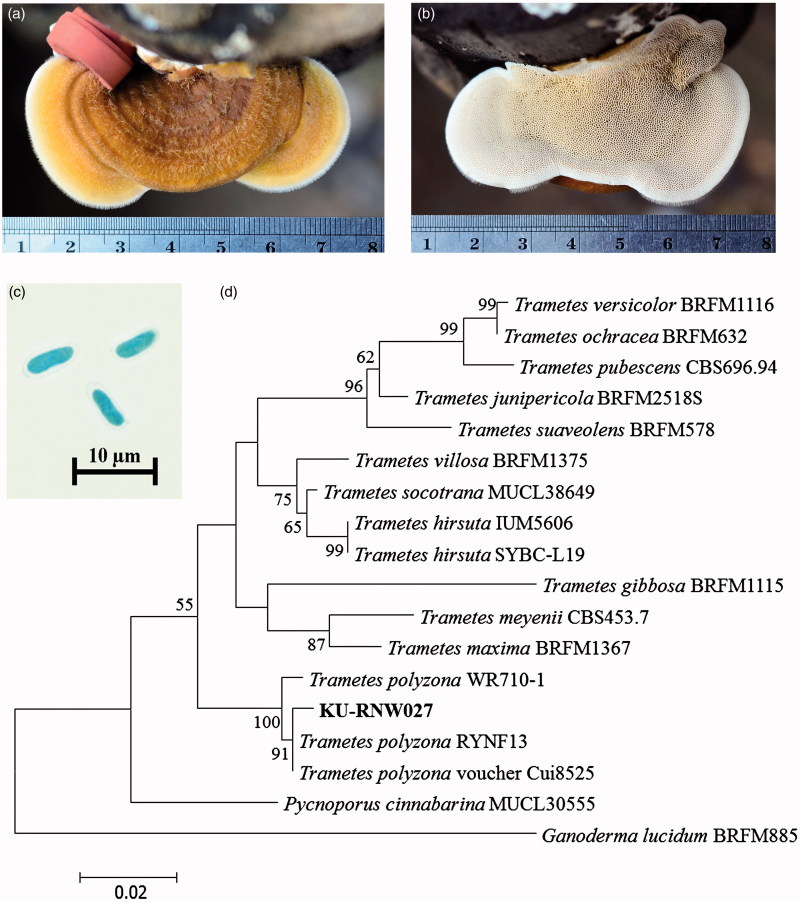
A newly remoted white rot fungal pressure KU-RNW027 was recognized as Trametes polyzona, primarily based on an evaluation of its morphological traits and phylogenetic information.
Aeration and fungal morphology have been essential components which drove pressure KU-RNW027 to secrete two completely different ligninolytic enzymes as manganese peroxidase (MnP) and laccase. Highest actions of MnP and laccase have been obtained in a steady shaking tradition at eight and 47 instances larger, respectively, than below static circumstances.
Strain KU-RNW027 existed as pellets and free type mycelial clumps in submerged cultivation with the pellet type producing extra enzymes. Fungal biomass elevated with rising quantities of pellet inoculum whereas pellet diameter decreased.
Strain KU-RNW027 fashioned terminal chlamydospore-like constructions in cultures inoculated with 0.05 g/L as optimum pellet inoculum which resulted in highest enzyme manufacturing. Enzyme manufacturing effectivity of T. polyzona KU-RNW027 relied on fungal pellet morphology as dimension, porosity, and formation of chlamydospore-like constructions.

Assessment of anti-inflammatory, lipid peroxidation and acute toxicity of extracts obtained from wild larger basidiomycetes mushrooms collected from Akure (southwest Nigeria).
Ethanolic extracts of three wild medicinal mushrooms, specifically Lenzites betulina (LET), Trametes versicolor (TET), and Coriolopsis polyzona (CET), collected from Akure, southwest Nigeria, have been assessed for his or her lipid peroxidation, anti-inflammatory, and acute toxicity results.
The inhibition of the formation of thiobarbituric acid reactive species (TBARS) by extracts was focus dependent and ranged from 86.99% to 92.18% at 1000 µg/ mL. The IC50 of the extracts was additionally within the vary of 222.81 µg/mL to 737.13 µg/mL.
The anti-inflammatory impact measured by inhibition of mice ear edema was larger and considerably completely different (P ≤ 0.05) than the management.
The acute toxicity check additionally revealed tolerance to the three ethanolic extracts by Artemia salina at concentrations of 10 µg/mL to 1000 µg/mL, aside from ethanolic extracts of LET and TET, which exhibited toxicity in opposition to this invertebrate at 1000 µg/mL.
This analysis has proven that ethanolic extracts of these three macrofungi may very well be good sources of protected and efficient antioxidant and antinflammatory brokers for biopharmaceutical exploitation.
