Cellular prion protein mediates impairment of synaptic plasticity by amyloid-beta oligomers.
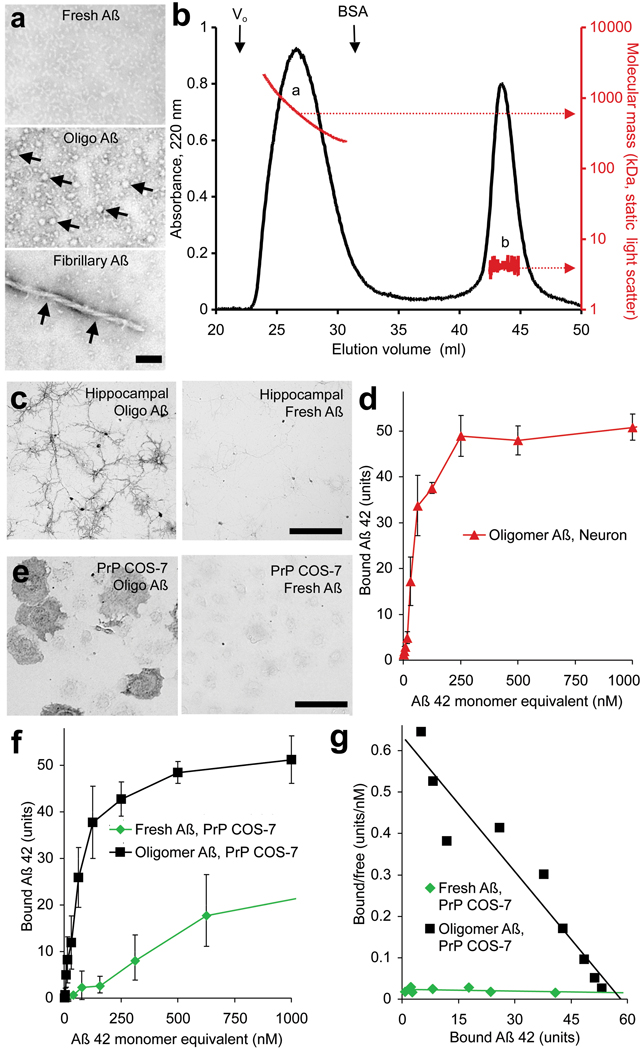
A pathological hallmark of Alzheimer’s illness is an accumulation of insoluble plaque containing the amyloid-beta peptide of 40-42 amino acid residues. Prefibrillar, soluble oligomers of amyloid-beta have been acknowledged to be early and key intermediates in Alzheimer’s-disease-related synaptic dysfunction. At nanomolar concentrations, soluble amyloid-beta oligomers block hippocampal long-term potentiation, trigger dendritic backbone retraction from pyramidal cells and…